Abstract
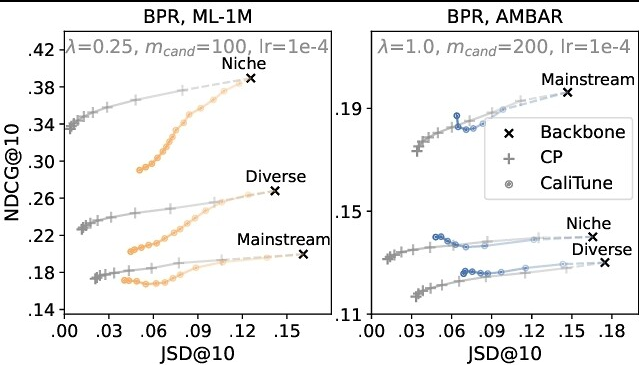
Calibration is the degree to which a recommender system is able to match the distribution of a certain item attribute among the items consumed by a user with their respective recommendations. Recent work suggests that many recommenders tend to provide miscalibrated recommendations. Furthermore, most approaches aimed at improving calibration adopt the post-processing paradigm, making them computationally costly at the inference time. This work proposes CaliTune, a fine-tuning approach applied to collaborative filtering based recommenders to allow them generate better calibrated recommendations without relying on costly post-processing. We compare CaliTune to an established post-processing approach on two backbone models and datasets from movie and music domains, focusing on popularity calibration. Our results suggest that CaliTune can offer a competitive accuracy–calibration trade-off in several settings, particularly when the backbone model exhibits high miscalibration and accuracy remains important, making it a promising inference-efficient alternative in such cases.
Citation
Oleg
Lesota,
Adrian Bajko,
Max Walder,
Matthias Wenzel,
Antonela
Tommasel,
Markus
Schedl
Fine-tuning for Inference-efficient Calibrated Recommendations
Proceedings of the Nineteenth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems,
1187 - 1192, doi:10.1145/3705328.3759319, 2025.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{Lesota2025CaliTune,
title = {Fine-tuning for Inference-efficient Calibrated Recommendations},
author = {Lesota, Oleg and Adrian Bajko and Max Walder and Matthias Wenzel and Tommasel, Antonela and Schedl, Markus},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Nineteenth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems},
publisher = {ACM},
doi = {10.1145/3705328.3759319},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3705328.3759319},
pages = {1187 - 1192},
month = {September},
year = {2025}
}
